Table Of Content
- Analysis of Variance:Table of Contents
- Author & Researcher services
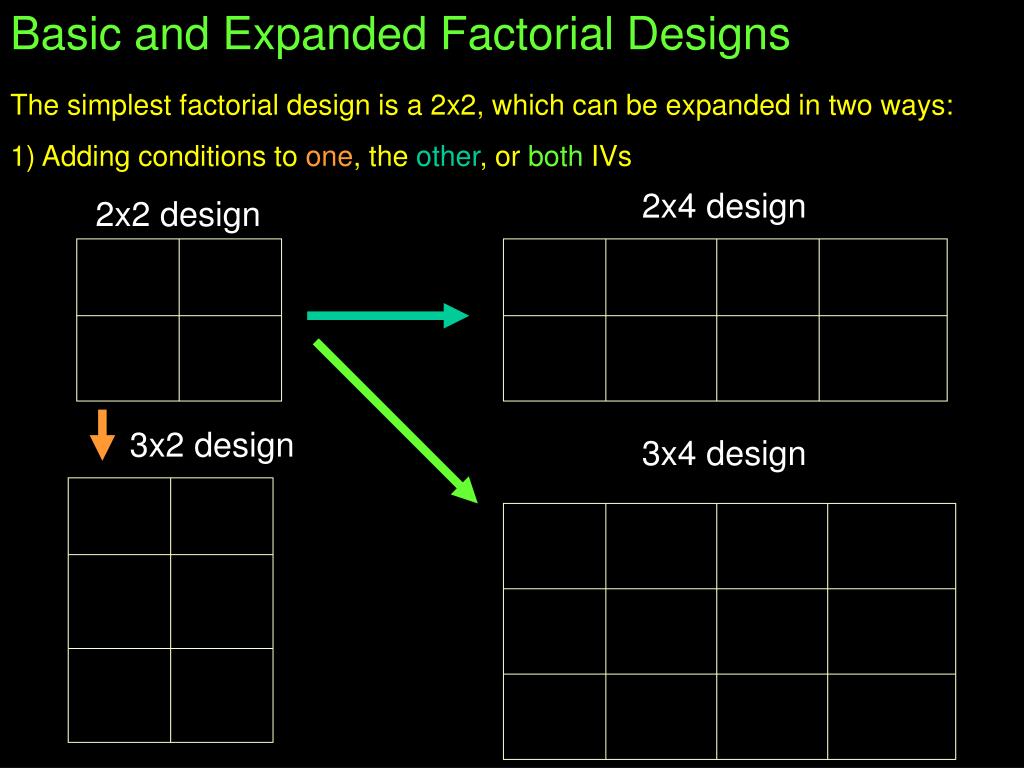
- Coding Systems for the Factor Levels in the Factorial Design of Experiment
- Creating a Factorial Design in Minitab
- Implementing Clinical Research Using Factorial Designs: A Primer
- Purpose of Experimental Design
- How to Interpret Causal Effects
- 2.5. Graphing the Results of Factorial Experiments¶
When you have an interaction effect it is impossible to describe your results accurately without mentioning both factors. You can always spot an interaction in the graphs because when there are lines that are not parallel an interaction is present. If you observe the main effect graphs above, you will notice that all of the lines within a graph are parallel. In contrast, for interaction effect graphs, you will see that the lines are not parallel. In addition, the efficiency of a factorial experiment depends in part on the extent to which higher order interactions are not found. If interactions are found, and inferential statistics must be used to unpackage such interactions, such simple effects tests would require examining the effects of ICs in only subgroups of the sample.
Analysis of Variance:Table of Contents

When there are two independent variables, each with two levels, there are four total conditions that can be tested. Often a researcher wants to know how an independent variable affects several distinct dependent variables. For example, Schnall and her colleagues were interested in how feeling disgusted affects the harshness of people’s moral judgments, but they were also curious about how disgust affects other variables, such as people’s willingness to eat in a restaurant. As another example, researcher Susan Knasko was interested in how different odors affect people’s behavior [Kna92]. She conducted an experiment in which the independent variable was whether participants were tested in a room with no odor or in one scented with lemon, lavender, or dimethyl sulfide (which has a cabbage-like smell). Although she was primarily interested in how the odors affected people’s creativity, she was also curious about how they affected people’s moods and perceived health—and it was a simple enough matter to measure these dependent variables too.
Author & Researcher services
Rather such experiments are used to identify the ICs that are amongst the best. Therefore, finding that several combinations of ICs yield promising effects is compatible with the goal of a screening experiment, which is to distill the number of ICS to those holding relatively great promise. In keeping with this, the data in Figure 1 suggest that we can winnow potentially promising combinations from 16, to 3. Which one of those three might be deemed most promising might be addressed via other criteria (effects on abstinence, costs, and so on) and in a follow-up RCT. A factorial design is often used by scientists wishing to understand the effect of two or more independent variables upon a single dependent variable.
Coding Systems for the Factor Levels in the Factorial Design of Experiment
Frank Yates created an algorithm to easily find the total factorial effects in a 2n factorial that is easily programmable in Excel. While this algorithm is fairly straightforward, it is also quite tedious and is limited to 2n factorial designs. Thus, modern technology has allowed for this analysis to be done using statistical software programs through regression. By the traditional experimentation, each experiment would have to be isolated separately to fully find the effect on B.
These runs are chosen carefully so that under the reasonable assumptions of effect sparsity and hierarchy, the terms of interest (e.g., main effects and two-factor interactions) can be estimated. In addition to looking at the employment sector, the researchers also look at gender. In this example, the employment sector and gender of the graduates are the independent variables, and the starting salaries are the dependent variables. So, for example, a 4×3 factorial design would involve two independent variables with four levels for one IV and three levels for the other IV. Other useful exploratory analysis tools for factorial experiments include main effects plots, interaction plots, Pareto plots, and a normal probability plot of the estimated effects. The advantage of multiple regression is that it can show whether an independent variable makes a contribution to a dependent variable over and above the contributions made by other independent variables.
New spectrofluorimetric analysis of empagliflozin in its tablets and human plasma using two level full factorial design - ScienceDirect.com
New spectrofluorimetric analysis of empagliflozin in its tablets and human plasma using two level full factorial design.
Posted: Fri, 27 Mar 2020 04:21:46 GMT [source]
As most of you know from regression the further apart your two points are the less variance there is in the estimate of the slope. The variance of the slope of a regression line is inversely related the distance between the extreme points. You can reduce this variance by choosing your high and low levels far apart. In these experiments one really cannot model the "noise" or variability very well.
Optimization and modeling of synthesis parameters of neodymium(III) bromide by dry method using full factorial design ... - ScienceDirect.com
Optimization and modeling of synthesis parameters of neodymium(III) bromide by dry method using full factorial design ....
Posted: Wed, 20 Dec 2017 18:38:04 GMT [source]
Purpose of Experimental Design
Overall, the purpose of experimental design is to provide a rigorous, systematic, and scientific method for testing hypotheses and establishing cause-and-effect relationships between variables. Experimental design is a powerful tool for advancing scientific knowledge and informing evidence-based practice in various fields, including psychology, biology, medicine, engineering, and social sciences. Of course, the researchers could also test, for example, 4 levels of concentration for the additive, and this would give 4 x 4 or 16 tanks, meaning 48 tanks in total. The quantities b1, b2, and so on are regression weights that indicate how large a contribution an independent variable makes, on average, to the dependent variable.
ANOVA is a statistical technique used to compare means across two or more groups in order to determine whether there are significant differences between the groups. There are several types of ANOVA, including one-way ANOVA, two-way ANOVA, and repeated measures ANOVA. Physiological measures involve measuring participants’ physiological responses, such as heart rate, blood pressure, or brain activity, using specialized equipment. These measures may be invasive or non-invasive, and may be administered in a laboratory or clinical setting.
Like Pareto plots, Half Normal plots show which factors have significant effects on the responses. The factors that have significant effects are shown in red and the ones without significant effects are shown in black. The further a factor is from the blue line, the more significant effect it has on the corresponding response. For wt% methanol in biodiesel, RPM is further from the blue line than pressure, which indicates that RPM has a more significant effect on wt% methanol in biodiesel than pressure does.
When compared to the one-factor-at-a-time design (OFAT), factorial designs are less expensive, more efficient, and produce more comprehensive results. The columns for AB, AC and BC represent the corresponding two-factor interactions. In the 2 × 3 example above, the degrees of freedom for the two main effects and the interaction — the number of columns for each — are 1, 2 and 2, respectively. Nature, he suggests, will best respond to "a logical and carefully thought out questionnaire". A factorial design allows the effect of several factors and even interactions between them to be determined with the same number of trials as are necessary to determine any one of the effects by itself with the same degree of accuracy. Regression analysis is used to model the relationship between two or more variables in order to determine the strength and direction of the relationship.
When we look at the normal probability plot below, created after removing 3-way and 4-way interactions, we can see that now BD and BC are significant. The surface plot shows us the same interaction effect in three dimensions in the twisted plane. In addition you can ask Minitab to provide you with 3-D graphical tools that will allow you to grab these boxes and twist them around so that you can look at these boxes in space from different perspectives. These procedures are all 'illustrated in the "Inspect" Flash movie at the beginning of this section. In visually checking the residuals we can see that we have nothing to complain about.

No comments:
Post a Comment